Building Hybrid Deep Learning Models for EEG-Based Seizure Detection
This article explores the design and implementation of a hybrid deep learning architecture combining CNN and Mamba Structured State Space Models (SSM) for EEG-based seizure detection, highlighting challenges, design choices, and real-world implications.
Introduction
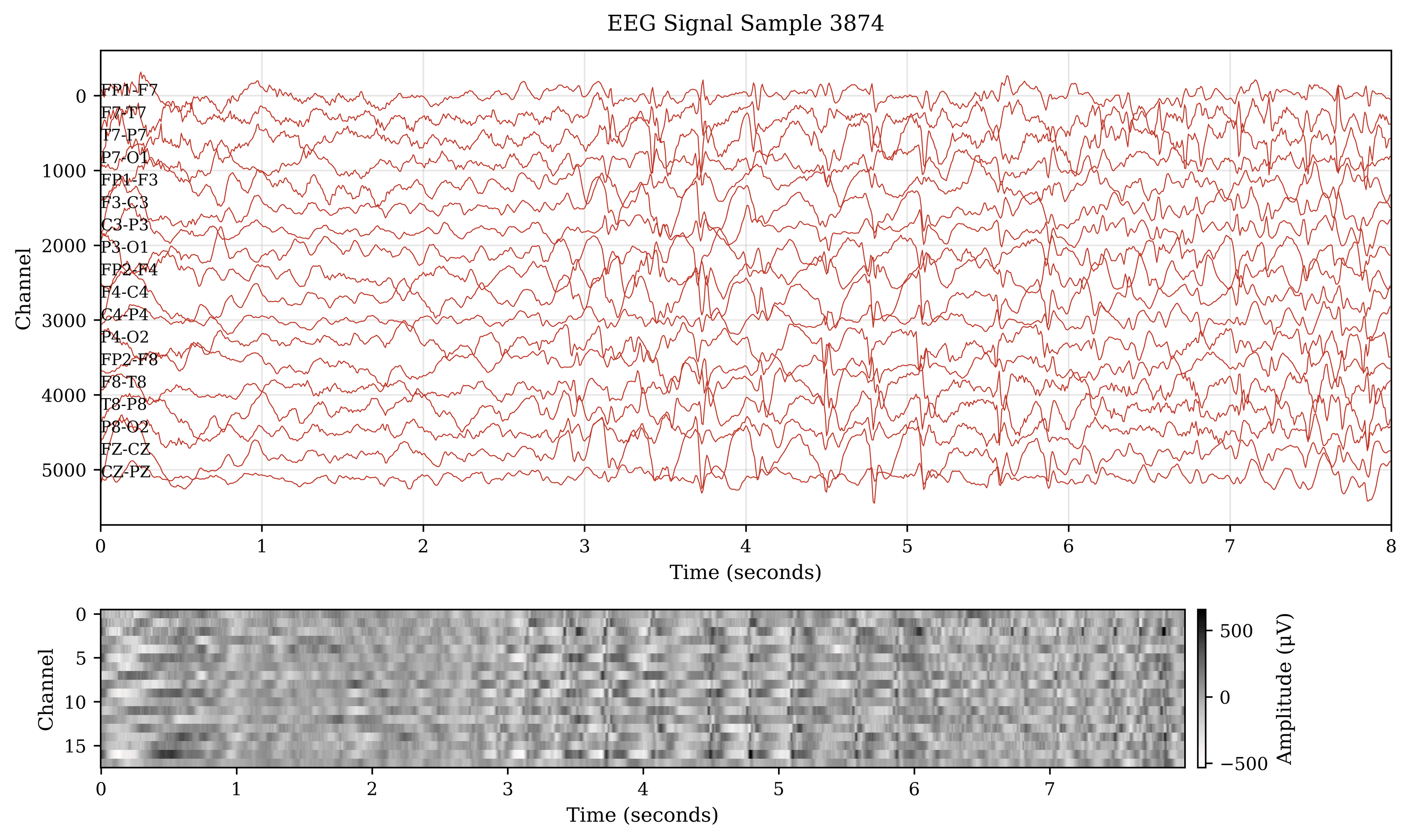
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures, affecting millions of people worldwide. Electroencephalography (EEG) is widely used to monitor brain activity and detect seizure patterns. However, manual analysis of EEG signals is time-consuming and prone to error, making automated detection systems a critical area of research.
In this project, I developed a hybrid deep learning model that integrates Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) with the Mamba Structured State Space Model (SSM) to improve temporal and spatial feature extraction from EEG signals.
Problem Statement
Traditional deep learning models face several challenges in EEG signal analysis:
- High temporal complexity and noise in EEG signals
- Long-range temporal dependencies that CNNs struggle to capture
- Class imbalance between seizure and non-seizure data
- Generalization issues across patients
The goal was to design a model capable of capturing both local spatial features and long-term temporal patterns while maintaining computational efficiency.
Model Architecture
The proposed architecture consists of three main components:
- Signal Preprocessing
- Noise filtering and normalization of EEG signals
- Segmentation of continuous signals into fixed-length windows
- CNN Feature Extractor
- Convolutional layers for extracting spatial and local temporal features
- Batch normalization and dropout for regularization
- Mamba SSM Module
- Structured State Space Model blocks for modeling long-range temporal dependencies
- Integration with CNN outputs to enhance sequential representation
This hybrid design allows the model to leverage the strengths of both CNNs and state space models.
Implementation Details
- Frameworks: PyTorch, TensorFlow
- Dataset: CHB-MIT Scalp EEG Dataset
- Evaluation Metrics: Accuracy, Precision, Recall, F1-score
- Training Strategy: Handling class imbalance using weighted loss and data augmentation
Results and Insights
The hybrid model demonstrated strong performance in seizure detection tasks:
- Improved temporal pattern recognition compared to baseline CNN models